Prevent saving changes to a file in Windows 7 (Protect files from modifications with Readonly)
![]() By default, any file you create in Windows 7 will be editable after the fact: in other words, anyone who has access to it can open it, view its content, make changes to it, and save the changes. But what if you have a file that you want to protect from modifications? A typical example is a sales form or other document that many people need to access, but that should remain intact for the next time they use it - users need to save a copy of the file, but leave the original untouched. Windows 7 makes this possible thanks to the "Read-only" (or "readonly") properties of files; you will also learn about the limitations of protecting files this way (and an alternative).
By default, any file you create in Windows 7 will be editable after the fact: in other words, anyone who has access to it can open it, view its content, make changes to it, and save the changes. But what if you have a file that you want to protect from modifications? A typical example is a sales form or other document that many people need to access, but that should remain intact for the next time they use it - users need to save a copy of the file, but leave the original untouched. Windows 7 makes this possible thanks to the "Read-only" (or "readonly") properties of files; you will also learn about the limitations of protecting files this way (and an alternative).
Make a file read-only, and prevent any modification
Follow these steps to protect a file (or group of files) from changes:
- First, navigate to the folder in which you have stored the file or files you want to protect from modification. We'll explain how to protect one file or protect multiple files at the same time.
- If you are trying to prevent changes to be made or saved to a single file, simply right-click on it, and choose "Properties" from the context menu.
To protect several files from modifications, you can either follow these steps for each file you want to make read-only, or (easier), see how you can select multiple files at the same time. After you have selected all the files you want to protect, right-click on any of them and choose "Properties".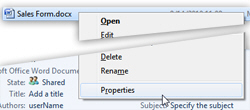
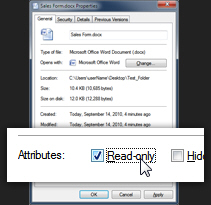
- Windows 7 will open the "Properties" dialog of the file, with the General tab automatically selected.
- Look at the bottom of this tab, for a section labeled "Attributes". It contains the "Hidden" checkbox, which allows you to hide files and folders in Windows 7; the "Read-only" checkbox is the one we're interested in for this tutorial; check it, and click on the "OK" button to apply the change.
- Your file -or selection of files- is now protected from any unintentional modifications; in our sales form example, someone who accidentally tries to save changes to the file will receive an error message telling them that the file cannot be edited or changed; at that point, they can use the "Save As" command to make a copy of the file, and save changes to that copy!
How elegantly the prevent-change feature is implemented depends on the program: Word 2007, for example, will simply display the Save-As dialog right away, without any explanation; other text editors may throw a cryptic error message - either way, your file is protected from editing.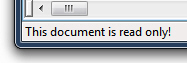
How effective is read-only to protect files from modifications and prevent changes?
Anyone who knows about the readonly property of files and folders in Windows 7 can manually "override" that setting by unchecking the "Read-only" checkbox in the file's properties (in which case the file reverts back to being editable).
In other words, read-only protects your files from being accidentally saved-over, but doesn't protect you from voluntary and/or malicious attempts at saving over an original readonly file.
A later tutorial will explain how to truly protect files from editing by using "Windows authentication" and "file permissions" - this is a bit more complex, but also more efficient a protection. For now, the readonly property, easy to access and easy to configure, will do!
up ↑